Business partner
- Business partner concept
- Business partner concept
- Project Organization Matters
- Is Business Partner a new concept?
- Principle of One
- Different Object Models
- Organizing Principles
- BP and Customer/Vendor Integration (CVI)
- BP Grouping, BP Roles, and Customer/Vendor Integration (CVI)
- Reconcilable or Irreconcilable Differences?
- Business Partner Numbers
- Contact Persons
- Screen Field Status
- Business Partner Design
- Data Migration of Business Partner
- Integration of ECC Customer / Vendor to S/4HANA BP
- Enhancement of Customer / Vendor
- Distribution of Business Partner: DRF
- Deleting a Business Partner
- S/4HANA Technical Conversion
- Data model
- Attributes
- Global Location Number (GLN)
- CVI
- CVI: Customer vendor integration
- 2797772 - S/4HC: How to access Business Partner Tax Number via CDS views
- How to find customer-supplier-bp?
- Business partner in application documents
- Customer
- Partner determination
- Branch/head office relationship (Billing document type)
- Customer hierarchy
- 1678189 - Customer hierarchy (VDH1N): Performance and technical info
- 2270657 - How to change hierarchy partner function
- 2687235 - Cannot Change Assignment of Parent Account
- 2882156 - Customer hierarchy level in KNVH table
- 2802125 - Hierarchy partners can only derived from the sold-to party
- 2409939 - S4TWL - Business Partner Hierarchy Not Available
- 3002283 - Customer hierarchy fields unavailable in BP transaction
- 548716 - FAQ: Customer Hierarchy
- Procurement
- Partner Roles in Purchasing
- Vendor Hierarchies
- 2309153 -BP_CVI: Guideline Version 1.14 for customer enhancements in CVI (customer/vendor integration) in SAP S/4HANA releases
- 2638067 - How to activate duplicate check for customer/vendor
- Sales
- 1927107 - No new partner determination when changing the partner
- 2959891 - No item partner allowed for standard item category TAS and TAB
- 2876039 - Following mandatory roles missing in partner maintenance: PI ME366'
- 394091 - Partners are not transferred from vendor master
- 459350 - FAQ: Partner determination in purchasing
- 1802012 - ME58, ME2*N - Partners are not determined / Saved to PO
- Logistics execution
- 2493272 - Ship-to party in STO - Outbound Delivery process
- 672142 - Partner transfer from customer master for purchase order as of Release 4.7
- Intercompany billing
- 141676 - No partner differentiation in intercompany billing
Business partner concept
We understand that Business Partner (BP) is the leading entity – the strategic object model – for all Customer and Vendor master records in S/4HANA. In fact, BP is the only visible entity.Source: Peeking Behind the Curtain of S/4HANA Business Partner – MDA Blog (masterdataaficionado.com)
Project Organization Matters
The first mistake that I made — on my first S/4HANA ERP implementation — was to continue thinking in terms of Customers and Vendors.Our project organized discussions and resources around Customers and Vendors, rationalizing that these were mainly separate legacy business objects, and certainly each had different business process concerns. What’s more, legacy Customers and Vendors had different stakeholders.
I won’t make that mistake again! At the very least, a single master data functional expert must have a comprehensive view and be completely responsible for BP design.
At best, you should be actively promoting the notion that enterprise-wide business process design suffers unless it’s clear that there’s one — and only one — BP design that comprehensively covers BP, Customer, and Supplier. BP is a single business object. Repeat the words until your friends begin repeating the words: BP is a single business object. In practice, that means a single functional expert, a single data owner, and a single view of data governance for BP.
To that end, even the words matter. I avoid saying “Customer” and “Vendor” in conversation when speaking about S/4HANA. Those terms are appropriate for legacy systems. For S/4HANA, I say “BP.” The designation is to be understood as all encompassing. It’s “BP Supplier” or “BP Customer,” if I need to be specific. Yes, you need to be specific.
Is Business Partner a new concept?
Principle of One
SAP S/4HANA Principle of One means providing a single solution for a given business requirement.
The necessity of applying this “simplification” concept -– simplification for the enterprise, but certainly not for you! — becomes apparent as applications using BP are brought into a central S/4HANA instance inhabited by Customers and Vendors. Beyond that, applications across the enterprise benefit from a common business object.
Different Object Models
An obvious difference is that the BP object model doesn’t include validity areas (views) for:- Customer – Company Code
- Customer – Sales Area
- Supplier – Company Code
- Supplier – Purchasing Organization
Redundant data is necessarily generated because SAP S/4HANA SD, MM, and more modules only use the classic Customer, Vendor, and related tables.
Organizing Principles
- Arranged mainly by BP Category and BP Grouping, which cannot be changed after the BP is created.
- BP Category designates whether the BP is a Person, Organization, or Group.
- BP Groupings are logical groupings of BP that share similar business process, but not necessarily the same system configuration requirements.
- BP are extended to Roles as needed (e.g. Supplier, Customer), limited by customizing and authorization.
- A single BP can comprehensively represent a Supplier, a Customer, both, or neither, as in the case of a BP Contact Person.
BP and Customer/Vendor Integration (CVI)
While gazing at the BP data model, take note of the blocks such as Address, Contact Persons, Tax Numbers, and Bank Details. When you see these attributes and objects at the BP level, it’s an indication that the data is maintained at the BP level with one-version-of-the-truth pushed down by CVI to the ERP Customer and ERP Vendor.
BP Grouping, BP Roles, and Customer/Vendor Integration (CVI)
CVI is the glue that holds these disparate objects together behind the scenes, and it’s implemented by configuring a hard link between BP Grouping and Customer and Vendor Account Groups.
A BP Grouping is linked through configuration to a Vendor Account Group and/or a Customer Account Group. Take notice of the singular. For a given BP Grouping, in the direction BP to Customer, you may assign one Customer Account Group. For a given BP Grouping, in the direction BP to Vendor, you may assign one Vendor Account Group.
CVI connects them with this hard configuration link. Number ranges across these objects immediately comes to mind as a pain point, but there’s much more to consider.
Reconcilable or Irreconcilable Differences?
Business Partner Numbers
As you work through a design, the Best Practice objective in end-state is that BP number, BP Customer number, and BP Supplier number are all the same number.This isn’t mandatory, and it may not be possible for legacy data.
Because MM and SD modules use Customer and Vendor number, not BP number, it’s significantly confusing for business users if there isn’t an alignment of numbers between these objects.
For example, if BP # 123 is extended to a Vendor Role (and Vendor # 456 is created) and extended to a Customer Role (and Customer # 789 is created), then imagine the confounding result as business processes are executed. A user would maintain BP # 123, but would have to create a Purchase Order using Vendor # 456, and perhaps create a Sales Order, a Credit, or a Debit using Customer # 789.
Contact Persons
Plain old Contact Persons are also created via CVI.
When you create a BP Person and then assign it in a Relationship as a Contact to a BP Organization, if the BP has Supplier or Customer roles, then a plain-old Contact Person is created by CVI for the plain-old Vendor or plain-old Customer. In fact, if the BP has both Supplier and Customer roles, then a plain-old Contact Person is redundantly created by CVI for both the plain-old Vendor and plain-old Customer.
If distributing BP, the number range for Contact Partners must be unique across all systems-clients in your landscape where distribution will occur.
The number range for Contact Partners must be assigned internally. Do not set the number range as external.
Number range can be checked in T-Code SNRO, object PARTNER (Number ranges for Contacts), Interval AP.
This point obviously requires planning and intentional execution.
Screen Field Status
The output of Business Partner Design is a clear definition of:
- BP Groupings and Number Ranges
- Identification of BP Groupings that include Customer Roles
- For each, what Customer Account Group and Number Range?
- Identification of BP Groupings that include Supplier Roles
- For each, what Vendor Account Group and Number Ranges?
I always like to begin with the objective in mind. So here it is: for at-a-glance clarity, you want to (eventually) produce a worksheet with these columns, with only 1 row per BP Grouping.:
- Legacy Vendor Account Group
- ECC Vendor Number Range
- ECC Vendor Number Range Internal/External
- ECC Vendor Number Range From/To
- Legacy Customer Account Group
- ECC Customer Number Range
- ECC Customer Number Range Internal/External
- ECC Customer Number Range From/To
- S/4HANA Business Partner Grouping
- Business Partner Number Range
- Business Partner Number Range Internal/External
- Business Partner Number Range From/To
- S/4HANA BP Supplier Acct Group (if Supplier role is valid for BP Grouping)
- Vendor Number Range
- Vendor Number Range Internal/External
- Vendor Number Range From/To
- Vendor Number Same Number (Y/N)
- S/4HANA BP Customer Account Group (if Customer role is valid for BP Grouping)
- Customer Number Range
- Customer Number Range Internal/External
- Customer Number Range From/To
- Customer Number Same Number (Y/N)
With this, I want see how legacy Vendors and Customers map into S/4HANA BP, BP Customer, and BP Supplier. And I want to see — across the board — how the BP Grouping, Account Groups, and number ranges are assigned without overlap.
SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit is the recommended tool for loading Business Partners into S/4HANA. Neither Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW) nor processing by a Intermediate Document (IDoc) is an option for data migration of BP.
SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit enables the load step, but all data migration steps must be considered:
- Analysis
- Extract
- Clean / Transform
- Validate
- Load
- Reconcile
Integration of ECC Customer / Vendor to S/4HANA BP
Enhancement of Customer / Vendor
For very specific details, refer to SAP Note 2309153 – BP_CVI: Guideline Version 1.14 for customer enhancements in CVI (customer/vendor integration) in SAP S/4HANA releases. This SAP Note includes a cookbook as an attachment.
Distribution of Business Partner: DRF
If your implementation is SAP Retail, then you’ll almost certainly (certainly, if you observe Best Practice) have a requirement to implement Site Master Distribution. This is a requirement, in part, to distribute Business Partners.
Deleting a Business Partner
To delete BP, use of the standard archiving process is mandatory (T-Code SARA).
T-Code BUPA_DEL is obsolete. Do not use T-Code BUPA_DEL to delete BP data!
Report BUPA_TEST_DELETE and function module BUP_BUPA_MASS_DELETE are obsolete.
Refer to these SAP Notes for background and process steps:
- SAP Note 2599676 – Transaction BUPA_DEL is obsolete
- SAP Note 2491026 – How to delete BP with vendor customer in S4HANA
- SAP Note 2640553 – How to delete BP without vendor customer in S4HANA
S/4HANA Technical Conversion
- SAP Note 2265093 – S4TWL – Business Partner Approach
- SAP Note 2743494 – Prevalidation: Master Data Consistency Check
- SAP Note 2832085 – New Central Cockpit for Customer Vendor Integration (CVI) to Business Partner
Attributes
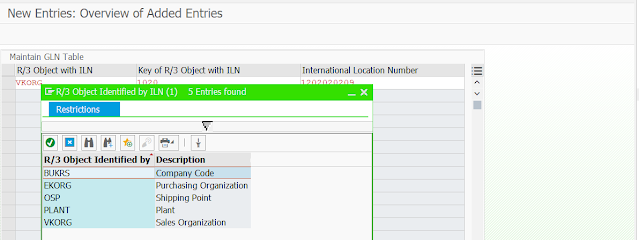
Global Location Number (GLN)
The Global Location Number (GLN), which is also called the International Location Number (ILN), uniquely identifies a physical, functional, or legal entity.A GLN is always linked to an address such as postal address, physical location, IP address, or e-mail address. Suchentities must be identified:
- In EDI messages
- When transport information about logistics units is transferred
- For printing bar codes that are to contain location information
- The GLN can be coded in EAN/UCC-128 symbols and attached as part of a bar code:
- At a physical location (ship-from location, warehouse, and so on)
- In addition to the Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC) in a logistics unit to identify the parties involved in the delivery process.
Examples of entities that are identified by a GLN are:
- Plant
- Customer
- Vendor
- Sales organization
GLN table( SPRO -> Maintain Global Location Number for Object )
To edit the vendor-specific GTIN, use the transaction EANVENDOR and specify the material and the vendor on the initial screen. Then choose a unit of measure and enter the GTIN. The system checks the GTIN to establish whether the check digits and prefix are correct.
Data model
Tables
Customer master data table
- General view- KNA1
- Finance View- KNB1
- Sales view -KNVV
Vendor master data table
- General view- LFA1
- Finance View- LFB1
- Purchasing view –LFM1
CDS views
CVI
How to find customer-supplier-bp
CDS views: I_BUSINESSPARTNERCUSTOMER, I_BUSINESSPARTNERSUPPLIEROther
The business partner category denotes whether a business partner is a natural person (private individual), organization (legal person/entity or part of a legal entity, such as a department), or a group. Depending on the business partner category, a certain set of fields has to be filled with data.
- BP role business partner, general to store data on a business partner who does not (yet) play any specific role for the company.
- A business partner in the BP role of contact person acts as an intermediary to an organization with which business contact is maintained.
- A prospect is a potential customer.
- The BP role Employee is the term for someone who works in your own company.
- The BP role Organizational unit maps units of internal structures in your own company.
- BP Role ‘Internet User’
A business partner relationship maps the business-relevant connection between two business partners.
Business Partner Relationship Category
- is contact person for
- is married to
- is temporary contact person for
- belongs to a shared living arrangement
- is identical to
...
Data cleansing allows you to compare, include, and merge redundant business partner master records.The possibility to archive and then delete business partners.
To evaluate customer hierarchies with the sales information system and in the profitability analysis, we can maintain the field Hierarchy assignment on the Marketing tab page in the customer master record for a hierarchy customer. Here we can maintain 10 features for hierarchy customers (HIEZU01 to HIEZU10).
During purchase order processing, the system automatically determines special partner functions in the partner data of the document. The system uses these partner functions for the following purposes:
There will be a default implementation which can be activated. If more features are needed, a new implementation needs to be created in ADDRESS_SEARCH BADI.
However, as of Release 4.0A, the system transfers only those partners that are marked as mandatory partners in the partner determination procedure.
This SAP Note now provides this function for Release 4.7 and higher.
Due to the fact that this is a modification that can be applied to a large number of release and Support Package levels, an automatic implementation using transaction SNOTE cannot always be guaranteed because the relevant context blocks can look different in the various levels. In such cases, you must implement the modification manually. Since the modifications are neither extensive nor complicated, however, this is not an issue.
CVI: Customer vendor integration
Maintain business partner number range in such a way that most numbers from customer or vendor stay unchanged:- Option 1 –Same BP number for customer/supplier
- Option 2 –New BP number (different from customer/supplier)
- Option 3 –Merge customer and supplier (SAP Note 2363892)
with customizing:
- If Customer and Vendor number ranges are overlapping →Maintain the business partner number range in such a way that the most numbers from customer or vendor stay unchanged.
- The defined number ranges are assigned to groupings in the Define groupings and assign number ranges activity.
- Assign BP roles to the account group for the customer master record in which the business partner is to be created when processing the customer
- For every customer/vendor account group a BP Grouping must be available
Business partner type is used for field selection ( per client, per BP role, per Activity, BP type )and grouping.
Address can be assigned to a transaction.
Identification Number ConceptDefine tax number categories for business partner master data, Define Tax Types and Tax Groups
The steps to maintain tax numbers with Tax Categories in App Maintain Business Partner are as follows:
- Business partner ( general: 000000 )
- Address data
- Identification ( External BP numbers )
- Bank details
- Status management
- Credit management ( UKM000 )
- Credit profile
- Creditworthiness data
- Credit segment data ( Differentiation )
- SD
- Customer number and account group
- Tax data
- Additional attributes
- Unloading points
- Texts
- Transport data
- Sales and distribution ( differentiation )
- Orders: Sales office, Item proposal, Currency, Price groups, Update group
- Shipping: Shipping cond, delivery parameters (under, over), partial
- Billing: Rebate, Pricing, Invoice list, Incoterms, Accounting group, Tax code
- Partner functions
- Status: set blocks
- Texts
- Documents
- Transportation: Defines whether or not the logistics service provider (LSP) declares the export at any time.
- FI Company code
- Payer
- Invoice receipt
- Procurement
- Legal data
- Vendor data ( number and group )
- Tax
- Texts
- Purchasing ( Differentiation )
- Supply region
- Purchasing data
- Partners
- Texts
- Relationships
2797772 - S/4HC: How to access Business Partner Tax Number via CDS views
CDS View I_CUSTOMER and I_SUPPLIER can be used to get the tax numbers. These CDS views provide fields TaxNumber1, 2, ..., 5 which are filled with the values inserted in tax categories. There is also a field in these CDS Views for VATRegistration.The steps to maintain tax numbers with Tax Categories in App Maintain Business Partner are as follows:
- Go to App Maintain Business Partner.
- Create or Open an existing BP in Business Partner (Gen.) role.
- Go to Identification Tab.
- Go to section Tax Numbers to maintain tax categories and its correspondng tax number.
- If the Tax Number maintained is for a country which is different than the BP country maintained, then KNA1 and LFA1 tables would not store tax numbers. Hence, in such scenarios, CDS Views I_CUSTOMER and I_SUPPLIER would return blank values.
Use: IBUSINESSPARTNERTOCUSTOMER
Business partner in application documents
Sales
Customer
Partner determination
During a cross-company-code business process, the following occurs:- In intercompany billing, the bill-to party (partner type BP) and the payer (PY) are the same as the sold-to party (SP) even though you defined different partner functions for intercompany billing in the master record of the customer.
- In intercompany billing (standard system), the (header) partner functions set for the bill-to party (BP) and payer (PY) are the same as those set for the sold-to party (SP).
One possible solution is the attached modification proposal in the include RV60AFZD, subroutine USEREXIT_NEWROLE_XVBPAK_AVBPAK.
Branch/head office relationship (Billing document type)
The indicator controls which partner functions of the billing document can be forwarded to Financial Accounting- initial : If the payer is different to the sold-to party, the payer is transferred to Financial Accounting as the customer and the sold-to party as the branch. Any branch/head office relationship stored in FI is ignored.
- A : The sold-to party is forwarded as the customer. Any branch/head office relationship stored in FI for this customer is taken into account.
- B : The payer is forwarded as the customer. Any branch/head office relationship stored in FI for this customer is taken into account.
Customer hierarchy
With customer hierarchies we can create flexible hierarchies to reflect the structure of customer organizations. We use customer hierarchies:
- for pricing determination (including rebate determination) and for creating statistics.
- to assign price conditions and rebate agreements to one of the customer’s subordinate levels, to to ensure that all subordinate levels are valid for the customer.
- for evaluations in profitability analysis (CO-PA) and in the Sales Information System (SIS).
To be able to display organizational elements, that are not independent partners, we can assign pure hierarchy nodes (account group 0012) in the hierarchy.
- higher-level customer
- dependent customers
In order to allow pricing via customer hierarchies, the hierarchy type must be assigned to the respective sales document type in Transaction OVH4. The hierarchy partners are only determined correctly if the higher-level functions are maintained correctly in the partner Customizing of the customer master. When you create with reference the hierarchy partners are only copied into the reference document if they exist in the partner determination procedure.
Field KNVH-HZUOR is not representing the level in the customer hierarchy. The KNVH-HZUOR is copied from the master data of the customer (KNA1-HZUOR). On the customer master (transaction VD03) you find this detail in the General Data on 'Marketing' tab.
Report RVKNVH00 can be used to graphically display the hierarchy.
Report RVKNVH00 can be used to graphically display the hierarchy.
T-codes: VDH1N, VDH2N.
Refer the below mentioned steps to check the CHtype:
To solve this, please do the following:
Only the sold-to party can be the source partner for customer hierarchy partners.
The Business Partner Hierarchy is no more available in S/4HANA. S/4HANA is in conceptualize stage for a better hierarchy solution.Customer Hierarchy Fields are not integrated into BP transaction and hence it's currently unavailable
Functions to work with Customer hierarchy
- RKE_READ_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_GET_CHILDREN BAPI Customer Hierarchy GetChildren
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_GET_ROOT BAPI Customer Hiearchy getRoot
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_GET_ROOT_LIST BAPI Customer Hierarchy getRootList
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_DEL BAPI Customer Hierarchy Delete
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_INS BAPI Customer Hierarchy Insert
- BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_UPD BAPI Customer Hierarchy Change
1678189 - Customer hierarchy (VDH1N): Performance and technical info
1.
General application information
You use customer hierarchies in sales order and billing document processing for partner and pricing determination (including rebate determination) and for creating statistics (-> evaluations in profitability analysis (CO-PA) and in the Sales Information System (SIS))
For more detailed information, read the online documentation.
2.
Customizing
In the SAP Reference IMG (Transaction SPRO) you need to maintain the following settings, using path
Sales and Distribution -> Master Data -> Business Partners -> Customers -> Customer Hierarchy ...
... Define Hierarchy Types
... Set Partner Determination For Hierarchy Categories
... Assign Account Groups
... Assign Sales Areas
... Assign Hierarchy Type For Pricing By Sales Document Type
3.
General technical information
For customer hierarchy maintenance and display, there exist the following dialog transactions:
Transaction Report
VDH1N and VDH2N RV_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY
Old: VDH1 and VDH2 RVKNVH00
(The old transactions VDH1 and VDH2 are not supported anymore from release 4.6B onwards.)
Customer hierarchy data are stored in database table KNVH with the following primary key fields:
Field Short Text
1. MANDT Client
2. HITYP Customer hierarchy type
3. KUNNR Customer
4. VKORG Sales Organization
5. VTWEG Distribution Channel
6. SPART Division
7. DATAB Start of validity period for assignment
In Standard there exists a no-unique database index A (Inverse repr. of customer hierarchy (subordinate nodes)) to improve performance of customer maintaining customer hierarchies.
Database table KNVH has the following technical settings:
Data class = APPL0 (Master data, transparent tables)
Size category = 3 (Data records expected: 150.000 to 620.000)
Buffering not allowed = 'X'
(Buffering of database table KNVH is not possible, because normally it is too large for buffering. Furthermore a buffered access is not necessarily faster.)
Please note: The following fields of databse table KNVH are stored redundant in the following database table fields:
Field Short Text DB table field
BOKRE ID: Customer is to receive rebates KNVV-BOKRE
PRFRE Relevant f. price determination ID KNVV-PRFRE
HZUOR Assignment to Hierarchy KNA1-HZUOR
This fact has consequences, which are discussed later (point 4.).
4.
Additional information / Restrictions
If you change one of the three redundant fields in customer master data (Transaction XD02, VD02), you receive I-message F2704 "Update customer hierarchy if change in rebate or price relevance" or W-message F2715 "Customer &1 active in customer hierarchy: Inconsistencies are possible" (both messages have a long text).
Therefore you have to update the customer hierarchy data (KNVH) in transaction VDH1N after such a change in customer master data by using menu path
Hierarchy -> Update programs -> ...
... Subhierarchy or
... All
This avoids issues due to inconsistencies between tables KNVH, KNVV and KNA1.
For further information (FAQ) on customer hierarchy and general restrictions (not related to performance), read FAQ note # 548716.
5.
Performance
Customer hierarchy maintenance/display (transactions VDH1N / VDH2N) was developed for a limited number of KNVH entries/nodes. But the hierarchy structure is the most important factor regarding performance! This is discussed below.
Note: In Standard there exists no additional room for improvement in the ABAP with regards to performance.
(Recursion is needed to display/adapt the assignments in a hierarchy tree -> inherent performance costs).
The display of a hierarchy tree is limited to 10.000 nodes.
But even this significant number of displayed nodes is not desired/reasonable from Standard point of view and therefore can cause performance issues.
So for large customer hierarchy trees displaying a complete hierarchy tree - starting from the top level customer - might not be possible.
To improve performance of customer hierarchy maintenance/display in VDH1N / VDH2N, we recommend that you
use as many selection criteria as possible and
enter a customer at the lowest possible hierarchy level and
use flag "Limit display to paths".
a) Assuming a fixed number of customer hierarchy (KNVH) entries, the following aspects regarding
hierarchy structure
have a positive influence on performance:
Several hierarchy types (KNVH-HITYP)
Large number of independent (small) hierarchy trees (-> many top level customers)
Several independent sales areas
Mininum number of hierarchy levels
Example:
100.000 Customer hierarchy (KNVH) entries:
Two different hierarchy types -> average hierarchy tree with 100.000 nodes divided by 2 = 50.000 nodes.
5 independent sales areas -> average hierarchy tree with 50.000 nodes divided by 5 = 10.000 nodes.
100 top level customers (= 100 independent hierarchy trees) -> average hierarchy tree with 10.000 divided by 100 = 100 nodes.
--> To maintain a hierarchy tree with 100 nodes is much faster as the maintenance of a hierarchy tree with 100.000 nodes (if the latter is possible at all).
a) To reduce the total number of customer hierarchy entries (KNVH) and therefore improve performance, you can check the following:
Use/Definition of Common Distribution Channels and Common Divisions for master data: Assign sales areas to each other -> A sales area shares its master data (e. g. customer hierarchies) with another sales area
Keep number of KNVH entries regarding validity periods to a minimum for the exact same assignment "Customer <-> Higher level customer" in the same sales area(s)
Example: 1. KUNNR = 1000 in sales area 1000/10/00 assigned to HKUNNR = 1200, valid from 01.01.2011 to 31.12.2011. 2. KUNNR = 1000 in sales area 1000/10/00 assigned to HKUNNR = 1200, valid from 01.01.2012 to 31.12.2012 -> Two KNVH entries. This is the same as KUNNR = 1000 in sales area 1000/10/00 assigned to HKUNNR = 1200, valid from 01.01.2011 to 31.12.2012 -> One KNVH entry.
Change customer hierarchies only if really needed (see above: Keep number of KNVH entries to a minimum ...)
Delete (old) customer hierarchy assignments, if they are definitely not needed anymore. Handle with care and read the online documentation!
Furthermore make sure, that your database accesses the customer hierarchy data (KNVH) in the best way possible (using up-to-date database statistics, etc.).
If customer hierarchy maintenance causes performance issues in dialog transaction anyway, you can try/test to maintain the hierarchy in background using the Standard BAPIs mentioned in FAQ note # 548716.
For example to assign a hierarchy sub-tree to another higher level customer please use BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_INS. This BAPI is less performance intensive (and easier to use) than using BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_UPD.
Furthermore please note, when creating a customer master in transaction XD01 / VD01, you directly can assign this customer to a higher level customer: Sales area data, Tab "Sales". But of course there are checks performed, if the assignment is possible!
(You find the necessary customizing regarding field status in transactions OVT0 and OB20.)
In addition - dependent on the customizing settings - customer hierarchy partners are selected in sales order processing (partner determination -> Function module SD_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY_PATH).
So large customer hierarchies can cause performance issues in transaction VA01, too!
The largest used customer hierarchy (highest number of KNVH entries) known to SAP Development and Development Support has about 250.000 nodes. But the hierarchy structure (see above) is not known!
Most customers have customer hierarchies with a total number of much less than 100.000 nodes (KNVH entries), but again the hierarchy structure is not known.
In any case we recommend to test customer hierarchy maintenance and hierarchy partner determination(!) before using it productive.
2270657 - How to change hierarchy partner function
You are not able to set the 'Mandatory' flag for partner determination in case you have maintained CHtype (Customer hierarchy type) V_TPAR_SD-HITYP as "A".Refer the below mentioned steps to check the CHtype:
- Goto tcode VOPAN
- Select 'customer master' and then click on change button
- Now double click on 'Partner functions'.
- Here check for Partner Function 1A, 1B, 1C...1E that CHType is set as 'A'.
To have the partner function in the list option in XD02 you have to delete the entry "A" in field V_TPAR_SD-HITYP (hierarchy type).
(In this document, accounts A, B and C represent the respective accounts in your system established in the same hierarchy.)
2687235 - Cannot Change Assignment of Parent Account
You have an account hierarchy set up where account A is parent of account B, which in turn is parent of account C. You wish to edit this hierarchy to put account C directly as child of account A, but find that to not be possible.(In this document, accounts A, B and C represent the respective accounts in your system established in the same hierarchy.)
This is the standard behavior of the hierarchy framework.
To solve this, please do the following:
- Edit account C.
- Remove account B from the Parent Account field.
- Save the changes.
- Now click Edit again.
- Click the value help for the Parent Account field.
- Search for account A.
- It will now be available for selection.
2882156 - Customer hierarchy level in KNVH table
- In transaction VDH1N or VDH2N you create a customer hierarchy OR you update the hierarchy level of a customer and save the changes.
- You expect that the KNVH-HZUOR (Assignment to Hierarchy) field will be updated and showing the current hierarchy level on which the customer is.
- Customer hierarchy data is only saved in table KNVH. The hierarchy level of a customer as a numeric value is not stored in the table, however, you can check the customer number of the higher-level node.
- Report RVKNVH00 can be used to graphically display the hierarchy.
2802125 - Hierarchy partners can only derived from the sold-to party
No source partner can be maintained for customer hierarchy partners in VOPAN.Only the sold-to party can be the source partner for customer hierarchy partners.
2409939 - S4TWL - Business Partner Hierarchy Not Available
Business Partner hierarchy is removed in SAP S/4HANA to avoid redundancy as customer hierarchy is already available for the applications to consumeThe Business Partner Hierarchy is no more available in S/4HANA. S/4HANA is in conceptualize stage for a better hierarchy solution.
3002283 - Customer hierarchy fields unavailable in BP transaction
- Goto transaction BP
- Enter the BP number or try to create a new BP
- Choose the BP role FLCU01 or any other custom BP role defined for customer sales area
- Click on 'Sales and Distribution' data
- Enter the Sales Area details
- In the Orders tab, following customer hierarchy fields are unavailable:
- Hierarchy Type, Higher-level customer, Valid from & Valid to
548716 - FAQ: Customer Hierarchy
1. Question: Is transaction VDH1N for maintaining the customer hierarchy capable of batch input?
Answer: No. Due to the control technology, transaction VDH1N is not capable of batch input.
However, you can use the following APIs:
'SD_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY_INSERT'
'SD_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY_CHANGE'
'SD_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHY_DELETE'
or as of Release 4.6C the BAPIs
'BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_INS'
'BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_INS'
'BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_UPD'
Note that the mentioned APIs are not released.
2. Question: The 'BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_INS' BAPI does not update all data records. What can I do?
Answer: If you call the BAPI in a program within a LOOP and update the BAPI directly, this must be done with a COMMIT WORK AND WAIT, since otherwise there are locking problems.
3. Question: Is there a message type for the distribution of customer hierarchies by IDoc?
Answer: No.
4. Question: Can I use transaction VDH1N (or VDH2N) to print the customer hierarchy or export it into a file?
Answer: No. Due to the new interface which uses the control technology, the print or export into a file using the new transaction is not possible.
You can still use the old transactions VDH1 and VDH2 to print the customer hierarchy. However, bear in mind that the old transactions are restricted (for example, limited number of hierarchy levels). As of Release 4.6*, we recommend that you use the new transaction VDH1N to maintain the customer hierarchy.
5. Question: Do change documents exist for the customer hierarchy (table KNVH)?
Answer: No. The customer hierarchy master data is time-dependent master data; that is, change documents are not required. In transaction VDH1N/VDH2N, you always receive the customer hierarchy which is valid at the selected validity date.
However, you have the option to react to business transaction events (BTEs) which are triggered during the maintenance of the customer hierarchy.
BTE 00504004 CREATED
BTE 00504005 CHANGED
BTE 00504006 DELETED
1. Node was created:
BTE CREATED
2. Node (attribute) was changed:
BTE CHANGED
3. Node key was changed:
BTE DELETED (Old node)
BTE CREATED (New node)
4. Node was deleted:
DATBI = DATBI - 1 ; BTE CHANGED
5. Node assignment was changed:
DATBI = DATBI - 1 ; BTE CHANGED (Old node)
BTE CREATED (New node)
If you want to develop a user-defined solution for this purpose, refer to your local consultant.
6. Question: Can I delete/archive "obsolete" KNVH records?
Answer: There is no function for deleting/archiving "obsolete" KNVH records in the standard system.
(You can, however, use the BAPI 'BAPI_CUSTOMER_HIERARCHIE_DEL'.)
7. Question: Why does the system exit transaction VDH1N after you save?
Answer: This is the standard-behavior of transaction VHD1N. For technical reasons, this cannot be changed.
8. Question: Why does the system not determine any hierarchy partners for certain sales document types (for example, quotations, contracts)?
Answer: The system can determine the hierarchy partners for all sales document types. However, as a prerequisite, you must assign a hierarchy type in Customizing: "Sales and Distribution -> Master Data -> Business Partners -> Customers -> Customer Hierarchy -> Assign Hierarchy Type For Pricing By Sales Document Type" (transaction OVH4).
Procurement
Partner Roles in Purchasing
You can assign these partner schemas to (only) different purchasing document types. This has the effect that only the roles of this schema can be maintained in documents belonging to this document type.\- Vendor (LF)
- Ordering address (BA): If you define another partner for the partner role BA, a standard PO or release order will not be sent to the address of the vendor (role LF) but to the ordering address of the partner.
- Goods supplier (WL)
- In the case of Intrastat:
- If you define a partner from another member state of the EU for partner role WL, standard POs or release orders will be taken into account when Intrastat declarations are created.
- In the case of a Return Delivery:
- If you define another partner for the partner role WL, the address of the goods supplier will be determined for return deliveries in Inventory Management.
- Invoicing party (RS): If you define another partner for the partner role RS, the invoicing party’s account will be charged instead of the vendor’s.
If you wish to use partner roles for price determination purposes, SAP provides the enhancement LMEKO001 (customer exit EXIT_SAPLMEKO_001).
You can then create a partner role "forwarder", for example, so that the freight charges of different carriers or forwarding agents can be taken into account in the purchase price determination process.
Vendor Hierarchies
For example, if your vendor base includes multi-level buying groups, cooperatives, or chains of retail outlets, you can create vendor hierarchies to reflect the structure of these groups.The vendor hierarchy category is used for the following purposes:
- To identify the purpose of a particular hierarchy
- To determine which vendor account groups are allowed in a hierarchy
- To determine which organizational data is allowed in a hierarchy
During purchase order processing, the system automatically determines special partner functions in the partner data of the document. The system uses these partner functions for the following purposes:
- To determine the hierarchy path and store it in the document
- To store hierarchy data per item (the pricing of individual items in the purchase order may relate to different hierarchy nodes)
2309153 -BP_CVI: Guideline Version 1.14 for customer enhancements in CVI (customer/vendor integration) in SAP S/4HANA releases
- Transaction SPRO -> Cross Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Business Partner Roles -> Define BP Roles.
- Define a BP role category as 'SLLSTL'. Specify the title and description as 'Person Responsible'. Specify business partner category as 'Person'.
- Next create a new BP role 'SLLSTL' with title and description as 'Person Responsible'. Specify BP role catogory as 'SLLSTL'.
2638067 - How to activate duplicate check for customer/vendor
For duplicate check functionality, it is necessary to activate ADDRESS_SEARCH BADI.There will be a default implementation which can be activated. If more features are needed, a new implementation needs to be created in ADDRESS_SEARCH BADI.
1927107 - No new partner determination when changing the partner
The system does not redetermine SH, PY, BP (ZA) partners with changes of the Ship-to party with sales documents.
The partner determination defined in transaction VOPA is only performed when the header record is being created for the sales document. This means that when a CHANGE is made on the partner screen, VOPA will not be called again.
This is the standard system design. If you need to have the item partner for those standard item categories, you may change it based on your own business requirement:
The partner determination defined in transaction VOPA is only performed when the header record is being created for the sales document. This means that when a CHANGE is made on the partner screen, VOPA will not be called again.
2959891 - No item partner allowed for standard item category TAS and TAB
- For a Third Party process, it is the third party partner who will make the delivery directly to the customer. So in this case the item partner and the header partner are expected to be the same. Hence the reason for standard item category TAS assigned partner determination procedure "T No Item Partner".
- For an Individual Purchase Order, it is the third party partner who will make the delivery to the SD-partner and then the normal delivery will be created from the sales order. So in this case the item partner and the header partner are expected to be the same. Hence the reason for standard item category TAB assigned partner determination procedure "T No Item Partner".
This is the standard system design. If you need to have the item partner for those standard item categories, you may change it based on your own business requirement:
- Change the partner determination procedure assigned to those categories
- Or add the partner function you want into the partner determination procedure "T"(No Item Partner)
2876039 - Following mandatory roles missing in partner maintenance: PI ME366'
Missing master data. A Supplier that has not been created for a company code must not be accepted as a partner in the purchasing documents for which a company code exists.
Extend your Supplier master data for the PI invoicing party to the Company code involved. This is done via webgui tile 'Manage Business Partner (BP)' business Partner FLVN00.
459350 - FAQ: Partner determination in purchasing
1. Question: Why are partners not determined from the vendor master/contract/reference when a purchasing document is created (purchase order, request for quotation, contract, scheduling agreement)?
Answer: See SAP Notes 37170, 394091, 376319 (for transaction ME21N), and 673062.
2. Question: Why are partners determined for another purchasing organization during the creation of a contract?
Answer: You create a purchasing contract, for example, for purchasing organization A. In the vendor master, several partners are maintained for the vendor for purchasing organization A. In addition, several partners are maintained for the vendor for purchasing organization B.
In transaction OMKJ, purchasing organization B is assigned as a reference purchasing organization to purchasing organization A.
In the detail for this assignment, the vendor master indicator is set. This indicator enables access to the info record of the reference purchasing organization. As a result, partner determination also determines partners for reference purchasing organization B. Please note that this function can only be used in an IS Retail system (provided the switch ISR_RETAILSWITCH is active)!
This function cannot be used for NON IS Retail systems.
3. Question: Why are the partners not displayed when you display a purchasing document even though the corresponding entries exist in the table EKPA? (Transfer of documents from legacy system during release upgrade).
Answer: Check whether the field EKORG (purchasing organization) is blank in the table EKPA for the entries for the purchasing document. If this is the case, you can use the report Z_CORR_EKPA to correct the inconsistencies.
You can obtain this report from SAP Support.
4. Question: Why are no partners determined and why do manually maintained partners disappear for a stock transport order or stock transport scheduling agreement?
Answer: See SAP Notes 117537 and 401734.
5. Question: Why does the system issue error message ME 266 ("Mandatory roles missing") in transaction ME21N even though in Customizing, no partner schema is assigned to the document type, so that partner determination does not take place?
Answer: See SAP Note 420058.
6. Question: Why is partner determination not carried out again in transaction ME22N after you change partner-relevant data such as vendor, purchasing organization and contract (with contract reference)?
Answer: See SAP Note 431351.
7. Question: Why are partners not determined when you create a purchase order using transaction ME59(n)?
Answer: In the vendor master, several entries are maintained for one partner role. If none of these entries is flagged as "default", none of these partners is copied to the document during purchase order generation in transaction ME59(n).
However, if you use transaction ME21 or ME21N to create a purchase order, a dialog box for the selection of a partner is displayed.
8. Question: Why are partners that have a block or a deletion flag for the client or the purchasing organization not used when you create a purchasing document?
Answer: See SAP Notes 673062, 563677, 743414, 938652, and 1446971.
9. Question: You create a purchase order and you manually maintain several partners. Why are the manual partners overwritten when you enter the plant?
Answer: After you implement SAP Note 761614, a new partner determination is performed if the plant is changed. This is necessary because a change of plant can result in a change of the partners. The system cannot distinguish between partners that are manually maintained and partners that are determined by the system. You must maintain the manual partners at the end of the document creation process.
10. Question: Why is the invoicing party not determined when you create a purchasing document?
Answer: See SAP Notes 938652, 1446971 and 1727168.
11. Question: Which partner roles are taken into account when you create a purchase order and different partner data is maintained for the plant in the vendor master?
Answer: If the purchase order is to procure for several plants, the partner role for the plant of the first purchase order item is taken into account.
For example, the partner role GS (goods supplier) is different in each plant. However, GS can only be entered once (ME 359).
Solution: Create purchase order items for one plant.
1802012 - ME58, ME2*N - Partners are not determined / Saved to PO
When Assigning a Purchase Requistion (PR) to Purchase Order (PO) in ME58, or saving additional Partners to new / created POs in ME21N, ME22N, these Partners are missing once the document is created / saved.
Although Partner Roles (PI, OA etc.) have been maintained in the vendor master, these same Partner Roles cannot be copied to PO when creating the PO with transaction ME58.
Adding these Partners to the created PO afterwards and saving does not work either, these are blanked / reset.
Use customizing path 'SPRO->Materials Management->Purchasing->Partner Determination->Partner Settings in Purchasing Documents->Assign Partner Schemas to Document Types' to find out the relevant Partner Schemas by document type.
Then, use customizing path 'SPRO->Materials Management->Purchasing->Partner Determination->Partner Settings in Purchasing Documents->Define Partner Schemas', select the Partner Schemas (from step 1), and set the flag 'Search at Higher Level' for relevant partner function (PI, OA, etc.).
Save these and exit.
Logistics execution
2493272 - Ship-to party in STO - Outbound Delivery process
- Outbound Delivery determines the customer number in Ship-to Party field and not the Ship-to Party Partner Function maintained in the Customer Master
- The Customer number determined in the Shipping tab of the STO is also the number that is maintained in the Ship-to Party field in the Outbound Delivery
672142 - Partner transfer from customer master for purchase order as of Release 4.7
In Release 3.0/3.1, during the creation of replenishment deliveries from stock transport orders, all the partners from the customer master of the ship-to party were copied to the delivery if they were specified in the partner determination procedure of the delivery.However, as of Release 4.0A, the system transfers only those partners that are marked as mandatory partners in the partner determination procedure.
This SAP Note now provides this function for Release 4.7 and higher.
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Object FUNC SHP_COPY_PARTNER_FROM_PREC_DOC
*& Object Header FUGR V50A
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& FUNCTION SHP_COPY_PARTNER_FROM_PREC_DOC
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Object FUNC SHP_COPY_PARTNER_FROM_PREC_DOC
*& Object Header FUGR V50A
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& FUNCTION SHP_COPY_PARTNER_FROM_PREC_DOC
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Object FUNC SHP_CHECK_PARTNER_COMBINATION
*& Object Header FUGR V50A
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& FUNCTION SHP_CHECK_PARTNER_COMBINATION
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Object Header FUGR V50A
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& FUNCTION SHP_CHECK_PARTNER_COMBINATION
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
Intercompany billing
141676 - No partner differentiation in intercompany billing
In intercompany billing (standard system), the (header) partner functions set for the bill-to party (BP) and payer (PY) are the same as those set for the sold-to party (SP).
Due to reasons of upward compatibility, a solution is not provided for the standard system.
For a differentiation of different partners, only a modification is possible. For more information, contact your SAP consultant. See also SAP Note 170183.
One possible solution is the attached modification proposal in the include RV60AFZD, subroutine USEREXIT_NEWROLE_XVBPAK_AVBPAK.







Comments
Post a Comment