Material requirements planning [rev]
- Prerequisites
- Planning concept
- MRP areas
- FAQ
- 185599 - Special procurement keys in MRP area
- Planning process
- BOM Explosion and Determining Dependent Requirements
- Material classification for setting MRP parameters
- MRP types
- Lot Sizing Procedures ~ generate an order proposal with that optimal lot size
- Rounding
- Scrap calculation
- Scheduling
- Running Material Requirements Planning
- Demand-driven replenishment
- MRP on S4/HANA
- FAQ
- MD04: Use ( 24.09.2021 )
- 457110 - FAQ: Source determination in purchasing
- 1567876 - Planned order conversion: MRP relevance
- 634038 - MRP: Returns order and delivery
- 2980392 - OPPR: Reduced number of parameters maintainable for MRP groups in S4
- 23922 - MRP: Creation indicator, purchase requisition or planned order
- 1975704 - Evaluating the material masters for MRP live
- 2640949 - How Single Discontinuation Works
- 2659649 - How Parallel Discontinuation Works
- 944616 - planning Mode 2: Some/All components lost in BOM Explosion
- 2047547 - MD04, MD05: Dependent requirement without planned order
- 819617 - MD04: Inspection lots not displayed for handling units
- Rescheduling (04.10.2021)
- How to check possible causes if MRP does not create any proposals (04.10.2021)
- Automatic assignment of Storage Location MRP Area to Material Master (05.11.2021)
Prerequisites
Planning file entry concept
The planning run and the scope of the planning run (which materials are planned in which planning run) are controlled by the planning file. Entry in the planning file is deleted (checkbox is reset) immediately after MRP run. Entry in the planning file is again activated when there is a change to material with respect to MRP.- It is not possible to create an overview over all actions in which the planning flag is set as this concerns far more than 50 actions, the list would become constantly larger and some calls occur only dynamically.
- If you do not change either quantities nor dates or storage locations during the conversion of a planned order into a production order, the situation did not change for the materials planning and no planning flag is set.
- Net change planning (NETCH): Determines that the material is taken into account in the net change planning run.
- Plng file entry NETPL: Means that the material is taken into account in the short-term planning horizon during the next net change planning run.
- Reset ord. proposals: Controls that existing procurement proposals (planned orders, purchase order requisitions and schedule lines) from the last planning run are deleted and recreated.
- Re-explode BOM: Controls the re-explosion of BOMs for existing procurement proposals (planned orders, purchase requisitions, delivery schedules) that came from the last planning run.
- Planning date: Date for planning.
MRP evaluation
- Stock Requirement List: It is a dynamic list, which shows the current status of requirements & sources for that material. So any changes in the procurements or needs will be shown in this list.
- MRP List: It is a static list, which shows the status of requirements & sources just after the MRP run. This list is not updated till the next MRP run.
Common questions
Planning file entries are not created automatically for MRP area
- The requirement class of the sales order has MRP indicator (NODIS) 1 or 2 - No relevant to MRP.
- To determine the storage location, use user exit USEREXIT_SOURCE_DETERMINATION (MV45AFZB). If the storage location is filled here, the system can fill the MRP area correctly, that is, depending on the storage location.
MRP area
185599 - Special procurement keys in MRP area
- MRP areas are activated at client level.
- Materials are assigned to storage location MRP areas.
- A special procurement key "Phantom assembly"
- or "Withdrawal from an alternative plant" is maintained
- in the plant material master segment.
- A special procurement key is maintained in
- the MRP area segment of the material master.
- For special procurement keys that are entered in the MRP area segment, material requirements planning for the MRP area takes into account only the settings that refer to an actual special procurement, such as stock transfer or subcontracting.
- Special procurement keys with settings that refer to the control of the BOM explosion, such as "Phantom assembly", are not taken into account if they are entered in the MRP area segment. In material requirements planning, these special procurement keys are used only from the plant material master.
- However, the system does not issue an error message.
FAQ
Planning process
BOM Explosion and Determining Dependent Requirements
The BOM is exploded and the dependent requirements are determined within MRP during the planning run, after the system has performed the procurement quantity calculation, lot-size calculation and scheduling.- You have created a BOM that has a valid period and area (see Period/Area of Validity of BOMs ).
- The BOM status is set to active for MRP (see BOM Status ).
- The BOM components are relevant for production (see BOM Items Relevant for Production ).
- You have maintained a selection ID for the priority of the BOM in Customizing for Bills of Material, in the IMG activity Define order of priority for BOM usages .
- The system determines the valid BOM that is to be used for the explosion and for determining the dependent requirements.
- Alternative items and discontinued parts are taken into account within the valid BOM=
- Special cases:
- If you work with variant configuration and you have created a super BOM for the standard product, the system plans the components of the configurable product when the BOM is exploded in the planning run
- Phantom assemblies are also taken into account when the BOM is exploded
- You can define for products with a high number of components that total requirements are to be generated when determining the dependent requirements. You can thus improve system performance during the planning run
- The system determines the date for the dependent requirements on which the components are to be available for the production .
- The system can determine the issue storage location for the components when the BOM is exploded. The system then displays this issue storage location in the component list for the planned order .
- Direct procurement and direct production of components are also triggered in the BOM explosion of the planning run .
- If necessary, existing revision levels are taken into account in the BOM explosion
Determining the Valid BOM
- The system checks which BOM usage in the plant has the highest priority
- For this usage, the system then checks whether there is a valid BOM for the explosion date. The explosion date is the planned start date of the planned order.
- If, for a particular production unit, you want to ensure that the total BOM structure is always exploded using the same explosion date and have assigned a BOM explosion number and fixed key date to the sales order, the planned independent requirement, or the planned order, the system chooses the BOM that is valid for this date (Fixed Key Date) .
- The system checks, whether the chosen BOM has the status active for MRP .
- If a multiple BOM exists, the system checks which alternative BOM corresponds to the preconditions of the alternative selection .
Determining the Valid BOM Items
- When the valid BOM is determined, the system checks the items to see if they require the creation of secondary requirements:
- If you have maintained alternative items, the dependent requirements of the alternatives are calculated according to the usage probabilities
- The system checks whether a BOM item is a discontinued material and, if necessary, diverts the requirements to a follow-up material
- In the planning run, dependent requirements are only created for BOM items that are relevant for production . The system copies only these items to the planned order (
- For variant configuration, the BOM that corresponds to the configuration of the sales order is exploded. Thus, the system only plans those components that are to be used in production as specified by the configuration from the super BOM
- If a BOM item is a phantom assembly , the dependent requirements of the higher-level assembly are directly passed on to the components of the phantom assembly. The phantom assembly itself is still not taken into account
- exactly one material is to be replaced by one follow-up material ( simple discontinuation ), or
- a group of materials is to be replaced by another group of materials ( parallel discontinuation ).
Calculating the Dependent Requirements Date
As the components and the assemblies are needed for the production of a higher-level planned order, they must be available by the order start date of this higher-level planned order.If no lead-time offset has been maintained, the system uses the order start date for the source planned order as the dependent requirements date for the components.
Storage Location Determination in BOM Explosion ( PP )
In order for the system to find the issue storage location for components in a BOM explosion in MRP or in a backflush in repetitive manufacturing, you can make the appropriate settings according to the assignment of storage locations in the plant.- In the BOM for the assembly or for the finished product, you have defined the production storage location for the component in the BOM item.
- If you have not defined a production storage location in the BOM item, you can define in Customizing for MRP or in Customizing for Repetitive Manufacturing which strategy the system is to use to find the issue storage location and from which location the components are to be withdrawn in the BOM explosion. You do this in the IMG activity Define stor.loc./supply area determination for BOM explosion
- If you have defined a production storage location in the BOM item for the withdrawal of the components, the system finds it during the BOM explosion and adopts it in the planning run. You can check it in the component overview for the planned order.
- If you have not entered a production storage location in the BOM item nor defined a strategy in Customizing, the system checks whether the production storage location has been maintained in the material master for the component and uses it as the issue storage location in the BOM explosion.
- If you have determined a strategy in Customizing and if no storage location has been defined, the system reads the MRP group for the assembly and determines the strategy for the storage location determination. The following strategies are available:
- If you set indicator 1 Only components (or no indicator) in Customizing, the system checks to see whether the production storage location has been maintained in the material master of the components and uses this as the issue storage location.
- If you set indicator 2 Only assembly , the system checks to see whether the proposal issue storage location has been maintained in the production version of the assembly or finished product. If this has been maintained, the system uses this issue storage location for all components of the BOM for the assembly or finished product.
FAQ
How to debug MD04?
The stock/requirements list (transaction MD04) displays all the MRP relevant documents and is builded with information from many different tables, belonging to different application areas (PP, MM, SD, QM, etc).When a record is found on the database, a PRUEFEN form (PRUEFEN_PLAF, PRUEFEN_VBBE, PRUEFEN_RESB…) is called to validate, check and adjust the record. If this record is relevant to MRP, it will be inserted into the internal table MDPSX at the end of the PRUEFEN form. BAdI MD_CHANGE_MRP data is also called here, to make a possible adjustment of this planning element.
After all the SELECT forms, there is the code related to forecast, sorting and PIR consumption. Note that BAdI MD_ADD_ELEMENTS is called here.
- MD_GET_KUND: Read customer information for sales orders;
- MD_GET_LIEF – Read vendor information;
- MDEZX_AUFBAUEN – Build the MRP elements texts, as they are displayed on the screen;
- MDSUX_AUFBAUEN – Build the MD04 period totals;
S4 /
Besides those changes, the code logic behind MD04 is still the same: The same function module AUFBAUEN_MDPSX_ANZEIGEN is called to read the planning elements from the database and the planning elements relevant for MRP will fill the internal table MDPSX.
The difference starts within the function module AUFBAEN_MDPSX_ANZEIGEN. Here, there is a new piece of code that checks if the system should use the classic logic or if should trigger the new selection built specifically for the HANA database.
This data selection logic happens in HANA and we would have to access HANA Studio to be able to debug this step, so we cannot see the actual selection in the ABAP debugger. We can see, however, that the database selection results will be stored in the internal table LT_MDPS, so if there if a planning element is already missing here, it means it was not selected from the database and the problem is most likely related to the database selection in the HANA stored procedure.
1825187 - MD04/MD05: Incorrect quantity for an MRP element
The available quantity for a planning element is empty in the stock-requirements list (transaction MD04) or in the MRP List (transaction MD05).Cause
The available quantity may not be affected by planning elements in the following situations:
- A purchase order or stock transfer order has stock type blocked.
- A purchase order or purchase requisition for a value-updated material has an account assignment.
- A planned independent requirement is within the period of adjustment.
- Material has a forecast-based MRP type (such as MRP type VV).
- You have an active implementation of BAdI MD_CHANGE_MRP_DATA.
- Dependent requirements are defined as not relevant to MRP on the material master.
- The sales order requirement class/type is not relevant to MRP.
- A purchase order with stock type blocked will only affect the available quantity if the blocked stock is defined as available for planning. You can find this setting on the customizing transaction OPPI.
- A purchase order or requisition with an account assignment for a value-updated material should not affect the available quantity. The value update customizing for the material type can be found on transaction OMS2.
- A PIR within the period of adjustment should not generate any replenishment proposal and it is displayed only for information purposes. You can change the period of adjustment in the customizing transaction OMPG.
- For a material planned using forecast-based planning, MRP only considers the forecast requirements. Other requirements are displayed but do not influence the available quantity. You should use a different MRP type if other requirements should be considered.
- With BAdI MD_CHANGE_MRP_DATA is possible to define if a planning element will affect the available quantity or not. If you have an active implementation of this BAdI, check your custom code accordingly.
- On the material master tab MRP 4 you can find the field MRP relevancy for dependent requirements (MARC-AHDIS). If this field is set to 1, dependent requirements will not affect the available quantity.
- Check the setting defined for the field NO MRP for the sales order requirement class/type customizing on transaction OVZG.
The MRP user exit M61X0001 implemented to exclude certain materials in MRP
Please go to transaction SMOD or CMOD to check if the user exit is implemented.Some BADIs are implemented to exclude the MRP requirements
The BADI MD_CHANGE_MRP_DATA contains many methods that can change or exclude the data read for net requirements calculation, e.g. the reservation, dependent requirements, planned independent requirements etc. Please go to transaction SE18, input the BADI MD_CHANGE_MRP_DATA into the field 'BADI Name', and click 'Display', go to menu 'Implementation' > 'Overview' to check if there are your own implementations, if yes, double click that to check the source code of relevant methods.Sales documents are not considered in MRP
In the example above, sales order 14144 is displayed but is not considered in MRP (No quantity is reflected in column 'Available Qty'.
It happens because the field 'No MRP' has value 1 'Requirement not planned, but displayed' in customization transaction OVZG as above for the required class of the sales document.
If that is blank, the sales document can be planned by MRP. If that has value 2, the sales document doesn't appear in transaction MD04.
To get the required class of sales document, check the requirement type in field BEDAE of table VBAP, go to customization transaction OVZH as following to find the requirement class by requirement type.
Then, the class, e.g. 030 in this example, can be checked in transaction OVZG.
In addition, the sales order is not considered in MRP if the schedule line category which doesn't allow MRP is set in the order even though field 'No MRP' is set to consider it in transaction OVZG for requirement class. In screen shot below, CP is the one allows MRP, CN doesn't.
The dependent requirements are not considered in MRP
There is dependent requirements (Order Reservations in this case) with quantity 100 in the screen below, but no proposal is created.After checking, it is turned out that the value 1 'Materials for dependent requirements are not planned' in the field 'MRP dep.requirements' of MRP 4 view of the material master as below.
Resetting the field can create the proposals by MRP.
No proposals are created for the requirement of PIR (Planned independent requirement)
The PIR exists as below in MD04, but proposals, e.g. planned orders, are not created after running MRP.
The 'Adjustment: Planned Ind. Reqmts' value 1 means that the period is calculated forward from today, and the field 'Adjustment Period: PIRs' is the period by working days.
E.g. Today is 29.09.2011, plus 7 working days forward it goes to 10.10.2011. Since the PIRs lie before this date they are not included in the MRP calculation and no proposals can be created for them.
There is a requirement from safety stock
There is a requirement from safety stock in MD04 but this is not considered in MRP as the screen below.If the material has a material group in the material master, please go to the customization transaction OPPR.
Input the plant and MRP group, then click the button 'Safety Stock', then the screen below is displayed.
If there is a value in the field 'Share SStk' as above, this means that the percentage of the safety stock can be used to cover the requirement.
e.g. there is a requirement of safety stock 100, and the 'Share SStk' has the value 100 in the OPPR, then the quantity 100 * 100% = 100 will be used to cover its requirement. Since this can cover the safety stock itself no proposals are needed.
SAP Note: 1890440 - Materials are not planned by MRP
1920439 - How are the subcontracting requirements displayed in transaction codes MD04 and MD05?
In the subcontracting process, the necessary materials for making subcontracting assembly need to be purchased by ordering company, then transfer to a subcontracting vendor.The subcontracting requirements of transaction codes MD04 and MD05 are displayed as the following example in 2 segments generally, one is the plant segment which represents the ordering company, another one is the subcontracting segment for the subcontracting vendor.
Basics
Material classification for setting MRP parameters
- Prepare a comprehensive list of all materials
- Segregate the materials to plan from those that aren’t worth the time, effort, or cost involved in planning
- Segregate them further by classifying them as A, B, or C types (ABC analysis)
- Analyze A-materials:
- What should the safety stock of this material be?
- How many days of planning window do I need so that the system doesn’t make any automatic changes to my production (or procurement) plan?
- When there is a requirement for material, how much should I plan (exact quantity, minimum quantity, maximum quantity, etc.)?
- How should the incoming sales orders consume my planning figures?
- Is this material make-to-stock (MTS) or make-to-order (MTO)?
- Do I need to produce this material for a specific project?
- Is this assembly produced in-house or at another plant of the company?
- How much scrap (percentage) does the production of a material generate for a product or subassembly, so I can incorporate that in planning?
- Should I also first forecast material requirements by using a forecasting tool and adjust forecast values before proceeding with material planning?
- Evaluate raw and packing materials
- What is the planned delivery time of this material?
- What is the receipt of the goods (GR) processing time?
- How much under-delivery and over-delivery of material is allowed?
- Is there a scheduling agreement or a contract (quantity or value) with a vendor for a material?
- Is there a quota arrangement in place, in the case of multiple vendors for the same material?
- For B- and C-type materials, consider using consumption-based planning or stochastic replenishment procedures
Transaction WPDTC can provide a comparison between the information that you’ve entered in the material master and the actual planned delivery time that the system recorded for each delivery.
- Material requirements planning
- Deterministic repl. procedure (MRP): PD, P1-4, and D1,M0-M4..
- No BOM explosion
- Master schedule line
- Consumption-based planning
- Re-order point
- Forecast based
- Time phased planning
MRP types
PD
P1, P2, P3, and P4
- Firming methods of existing procurement proposals (within the planning time fence)
- Firming methods of new order proposals (within the planning time fence)
Delete firm planned orders ( if they are not converted during a period of time ) option from the Roll forward.
It is set in MRP Group or in the material master.
VB Manual reorder point planning
The reorder point quantity is your estimated consumption within the TRLT plus the safety stock quantity.
VM Automatic reorder point plng
V1 Manual reord.point w. ext.reqs
MRP type V1 acts exactly like VB, except that it takes external requirements into consideration.V2
It calculates safety stock and reorder point automatically using the Forecasting screen in the materialmaster record.
VV
In MRP type configuration, you can choose the type of historical consumption of material for planning whether the system uses total consumption or unplanned consumption. You can also choose the reduction method for forecast requirements.- Constant model (D)
- Trend model (T)
- Seasonal model (S)
- Seasonal trend model (X)
- Moving average (G)
R1 Time-phased planning & R2 Time-phased w.auto.reord.point
Lot Sizing Procedures ~ generate an order proposal with that optimal lot size
- Static lot-sizing procedures
- Lot Size: EX (Exact Lot Sizing)
- Lot Size: FX (Fixed Lot Sizing)
- if the lot size is 10 and req. is 90, then 9 proposals are generated
- Lot Size: FS (Fixed Lot Sizing with Splitting)
- Lot size is 10 and rounding is 20, then 5 proposals; takt time is to delay the start date for each proposal
- Lot Size: HB (Replenish to Maximum Stock Level)
- define the maximum stock level. It will check demands and adds req. to a proposal to have the stock in the max, qty.
- Periodic lot-sizing procedures: D, W, M
- aggregate demands for a period
- Optimum lot-sizing procedures
- fixed lot size costs, such as setup costs for machines or PO costs and variable costs: Variable costs = Requirement × Price × Storage costs [%] × Storage duration ÷ 365
Rounding
Scrap calculation
Assembly scrap
MRP1: Assembly scrap (%)- The system considers it during scrap calculation by correspondingly increasing the production order quantity.
Component scrap
Safety Stock
The safety stock must always be available to cover for unforeseen material shortages or unexpected high demand.static (i.e., absolute) safety stock
The Stock/Requirements List in Transaction MD04 subtracts that safety stock in the first line and then works without.
To avoid the unnecessary creation of planned orders for a smaller quantity, which can otherwise be covered by the safety stock, you can define the percentage (share) of safety stock.
To define the safety stock parameters, use configuration (Transaction SPRO) menu path, Logistics > Production > Material Requirements Planning > Planning > MRP Calculation > Stocks > Define Safety Stock Availability.
dynamic safety stock by use of the Range of Coverage profile ( Transaction OMIA )
- Dynamic safety stock = Requirements in the specified periods ÷ Number of days in the total period length× Range of coverage
Safety time
For days’ supply/safety time, the system plans the goods receipt in advance by the period specified as safety time. Thus, planned days’ supply of the stock, in fact, corresponds to the number of days specified as safety time. The system shifts backs the date of the receipts by the number of working days and also takes the factory calendar into account.Example: If you define that a 10% safety stock can be used to account for smaller shortages, which for this example means that 4 PC come from safety stock, then the system can cater to this small requirement or shortage of 2 PC from the 4 PC available from safety stock and no longer creates a procurement proposal.
Scheduling
Scheduling In-House Production
- Basic date determination ( based on the production time defined in the material master )
- The scheduling margin key (SMK) is the float consisting of the number of days it takes to release a production order and the number of days before and after production when the material finally becomes available.
- Quantity-Independent In-House Production Time or Quantity-Dependent In-House Production Time ( => In-house production time = Setup + (Order quantity ÷ Base quantity) × Processing time + Interoperation time )
- Lead time scheduling ( on the information in the routing (or master recipe) ) + perform capacity planning, sequencing, leveling, and scheduling with planned orders
Scheduling External Procurement
- Opening period
- Purchasing department processing time (Plant parameters)
- Planned delivery time
- GR processing time
Procurement Proposals
Planned order
Create a planned order
PR
Configuration Settings for Material Requirements Planning
- Activation: Transaction OMDU
- SAP IMG/Production / Material Requirements Planning / Planning / Define Scope of Planning for Total Planning
- Plant parameters
- MRP groups
- Material master (MRP views)
Running Material Requirements Planning
- Check the planning file to avoid planning materials that aren’t needed.
- Determine the material shortage quantity (or surplus quantity) by carrying out a
- net requirements calculation.
- Calculate the procurement quantity to include lot sizes for planned orders or purchase
- requisitions.
- Schedule basic dates or lead time (for in-house production only).
- Select the source of supply by determining the procurement proposal.
- Determine the requirement of subordinate parts on the basis of the bill of materials
- (BOM) explosion by carrying out a dependent requirements determination.
Demand-driven replenishment
MRP on S4/HANA
- Classic MRP
- Live MRP
- Stored procedures on SAP HANA
- The most important key differences between MRP live and classic MRP are mentioned below:
- MRP Live on HANA cannot plan materials that are included in supersession chains. In this case, the system also does not automatically plan the material using classic MRP. Use transaction MD_MRP_FORCE_CLASSIC to make sure that the material is planned using classic MRP.
- Customer can use classic MRP for Direct production since it is not yet supported by MRP Live on HANA
- Characteristics-based forecasting is not supported in MRP Live on HANA.
- Currently, MRP live does not write MRP lists
- Multi-level, make-to-order planning (transaction MD50) is not optimized for HANA.
- Individual project planning (transaction MD51) is not optimized for HANA.
- The creation indicator for purchase requisitions is not available in MRP Live. MRP Live always creates purchase requisitions if the material is procured externally.
- The creation indicator for delivery schedule lines is not available in MRP Live. MRP Live always creates delivery schedule lines if a valid delivery schedule exists.
- MD01N (MRP Live) is a standard SAP transaction code optimized for SAP HANA available to use with SAP S/4HANA system.
- Long Term Planning (LTP) is not supported by any HANA optimizations. That means it is neither possible to plan LTP scenarios in the context of MRP live nor SAP provide optimized database accesses when reading LTP data for the classic LTP transactions as we do it for appropriate MRP transactions. So there are no special LTP features at all in a HANA environment.
- MRP live
- it’s not possible to replace multilevel, make-to-order (MTO) planning (Transaction MD50) and the individual project planning (Transaction MD51) with MRP Live.
Requirement lists
Additional information
1567876 - Planned order conversion: MRP relevance
In Customizing for the order type-dependent parameters for process orders or production orders, you have set the indicator for the MRP relevance (Reservation Relevance/Generation of Purchase Requisition) to 2 "From release".You then use this order type to convert a planned order to a production order or a process order. In the planned order, reservations are always MRP-relevant.
You do not want the reservations to lose their MRP relevance during the planned order conversion, so you do not make any settings for system message C2 280. However, you also do not want purchase requisitions to be created until the order is released.
634038 - MRP: Returns order and delivery
- Customizing of the returns order (Allocation of the delivery type, in the Standard system NLR for the stock transfer case and RL for the return to vendor)
- Item category determination in the Customizing of the delivery (in the Standard system NLRN for delivery type NLR and RLN for delivery type RL)
- By means of the allocation of the requirements type to the activity, you must make sure in case of a stock transfer that you select a requirements type in such a way that by the assigned requirements class a requirement is generated which is relevant for the materials planning.
- For the problematic nature of the ATP (visibly in CO09), consider question 4 from Note 606282 after the creation of the delivery.
- For the return to vendor, a requirements type must be selected in case of which the assigned requirements class does not result in a requirement that is relevant for the materials planning.
- If you desire a delivery relevant for requirements for the return to the vendor from reasons of the ATP and if the Customizing is correspondingly prepared, as a consequence both the purchase returns and the delivery are regarded as a relevant requirement. This behavior cannot be avoided in the R/3 standard system(see Note 606282, question 6) and can be avoided only via a modification within the MRP.
2980392 - OPPR: Reduced number of parameters maintainable for MRP groups in S4
- Strategy Group (T438M-STRGR)
- Planning Horizon (T438M-PLAHZ)
- Direct Procurement Indicator (T438M-KZDRB)
23922 - MRP: Creation indicator, purchase requisition or planned order
- MRP group
- Plant
- Initial screen
- Planning -> Creation Indicator
- Planning -> Procurement Proposals -> Define External Procurement -> Plant:
- Creation of delivery schedules.
- Planning -> Activate Runtime Statistics
1975704 - Evaluating the material masters for MRP live
2659649 - How Parallel Discontinuation Works
Configuration:
- Set up follow-up materials and discontinued materials. Follow-up material is as normal. Set discontinuation fields for discontinued materials.
- Set "Discontinue indicator" as 1 for main discontinued material in the group, and "effective date" and "follow-up material".
- Set "Discontinue indicator" as 3 for dependent discontinued materials in the group, "effective date" and "follow-up material" is initial.
- Configure discontinuation data in BOM. From Item details screen, menu -> Extras -> discontinuation data.
Test:
- Confirm the stock for discontinued material(qty=0) and follow up material(qty=100).
- Run MRP for header material in T-code MD02.
- Check the planned order generated and switch to Component Overview. The requirement qty is transferred from Discontinued materials to Follow up materials.
- Result: Requirements for discontinued materials are transferred to follow-up materials.
Function:
- Parallel discontinuation transfers requirements for both materials in discontinuation group to follow-up material in follow-up group, only if stock is missing for the discontinued material with discontinued indicator "1". Discontinued material with discontinued indicator "3" is just dependent mateiral in the parallel discontinuation.
2640949 - How Single Discontinuation Works
Configuration:
- Create follow up material.
- Create discontinued material and assign follow up material to it.
- Configure discontinued material in BOM of Header material.
- Simple discontinuation is a 1:1 replacement of the discontinued part by the follow-up part at a particular date. It can be considered as a simple replacement of the material number only (MATNR). All other characteristics are inherited from the discontinued part. Based on that both materials should have the same characteristics from planning point of view.
Test:
- Confirm the stock for discontinued material(qty=0) and follow up material(qty=100).
- Run MRP for header material in T-code MD02.
- Check the planned order generated and switch to Component Overview. The requirement qty is transferred from Discontinued material to Follow up material.
- Notice: All other settings are inherited from the discontinued material, e.g. component Scrap 20% etc.
944616 - planning Mode 2: Some/All components lost in BOM Explosion
- the requirements element (Example sales order) has got configuration(CUOBJ) or parameter Effectivity(TECHS) attached to it.
- The BOM is using ECM(with Parameter Effectivity) or Object dependencies.
- Subcontracting Schedule lines are configured as procurement elements for the requirements.
- When using subcontracting with schedule lines , do not use the BOM having parameter effectivity or object dependency .
- If you want to use parameter effectivity or object dependency then have the purchase requisition/Purchase order as the procurement element.
2047547 - MD04, MD05: Dependent requirement without planned order
819617 - MD04: Inspection lots not displayed for handling units
The direct result of this is that inspection lots cannot be taken into account in transaction MD04.
457110 - FAQ: Source determination in purchasing
MD04 Use
Set a manual firming dateSorting and filter
- OM0J - Declaration Display Filter
- OM0I - Declaration Selection Rule
Der Unterschied zwischen Filter- und Auswahlregeln liegt in der Berechnung. Selektionsregeln kann sich auf die verfügbare berechnete Menge auswirken (!) .
Business function LOG_PP_LMAN
- Only when the material exists in product group, or exists in multiple plants, “Production Group” or “Cross-Plant View” appears. You should set corresponding customizing. The path is OPP1 -> Evaluation -> Display Material Groupings. Function Filter and Selection Rule can be used together.
Then in t-code MD04, “Product Group” tab appears. You can view the stock/requirement situation for multiple materials there. Also, you can decide if it is displayed in aggregated form or not by clicking the aggregation icon.
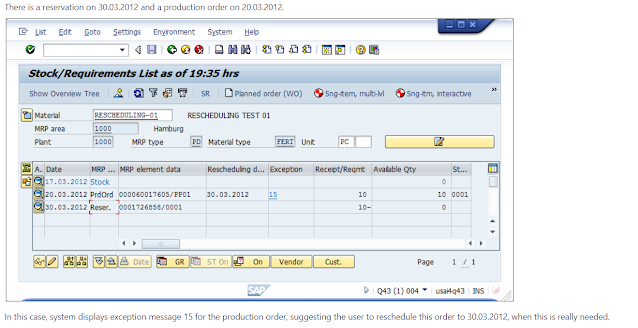
If a fixed replenishment element is found, an exception message is created, suggesting the user to reschedule this fixed element in order to cover the shortage.
System first searches for fixed elements before the requirement date. If a fixed element is found before the requirement date, then this receipt is not needed until later. In this case, the exception message “15 – Postpone process” is displayed for the element.
If the fixed element is after the requirement date, within the rescheduling horizon and this type of fixed element is included on the rescheduling check, according to the customizing, exception message “10 - Bring process forward” is displayed for the element.
Firmed elements: You can define which specific elements will be included on the rescheduling check. If the flag is unchecked, MRP will not consider the element during the rescheduling check.
Dependent reservations with positive sign (by-products or co-products) are not considered during the rescheduling check on the standard system. The system behavior can be changed with the implementation of the modification note 203151.
Comparison values: If the difference between the requirement date and the firmed receipt element is less than the tolerance value, system will not display an exception message.
The rescheduling horizon and the firmed elements can also be defined at MRP Group level.
It is also possible to reach the rescheduling customizing for the plant through transaction OPPQ and for the MRP group through transaction OPPR.
At last, even if there is no MRP group assigned to the material master, the settings defined at MRP group level will be consider if the MRP Group key is equal to the material type (see note 34013 for more details). For example, if the material type is ZPRD and there is an MRP Group ZPRD, the settings from this MRP group will be considered by MRP if the field MRP Group is empty on the material master.
1745312 - MRP creates redundant proposals though there are fixed future receipts which can cover the requirements
A new proposal (planned order, purchase requisition, schedule line etc.) is created to meet the requirement after running MRP though a fixed future receipt element exists already (firmed planned order, firmed purchase requisition, firmed schedule line, production order, purchase order etc.) at the date later than the requirement on the time axis. As a consequence, the exception message 20 (Cancel process) appears in MD04/MD05 for the fixed element,Here is the screenshot of transaction OMDT where the purchase processing time is maintained as 1 working day now.
25388 - MD01, MD02, MD03: Rescheduling proposals: Documentation
Symptom
1794796 - Planning calendar is not considered in rescheduling check of MD04
In MD04, the rescheduling date of the receipt element is based on the requirement date.
The logic in form CHECK_VWVER of program SAPLM61R is passing the requirement date to rescheduling date directly without checking the planning calendar.
How to check possible causes if MRP does not create any proposals
MRP sometimes does not create any proposals, e.g. planned order, purchase requisition, schedule lines, even though there is shortage for requirements. The root causes are not so clear.Here are some cases can be checked one by one.
Case 1: The total planning of MRP cannot generate any proposals
If you ran the total planning of MRP, e.g. MD01 or MDBT and no proposals were generated, please run MD03 for the material/plant, if this can create it means that the planning file entries of the materials are missing or the corresponding planning indicator, e.g. NETCH is missing in the planning file entry. Please go to the transaction MD21to check if the planning file entry exist, if there is not or no NETCH indicator is set then the system may not run the material in the total planning of MRP.
When the user run the total planning of MRP with the parameter NEUPL the system only runs the materials whose planning file entries exist (In this case, the NETCH indicator is not checked.). When the total planning of MRP is done with parameter NETCH, only the materials whose planning file entries exist with indicator NETCH are planned. But if you run MD03, the system does not check planning file entry since the system is told what material should be run.
Please create the planning file entry in MD20 or make some changes of MRP related object in order to set the flag. Running the transaction MDAB can automatically detect the missing planning file entries and create them but this does not set the NETCH indicators for the existing planning file entries.
Normally the planning file entry will be created automatically while the material is created or set the flag automatically when user make changes of MRP related.
The following note provides more details about the planning file entry:
SAP Note: 1890440 - Materials are not planned by MRP
Case 2: There is a requirement from safety stock in MD04 but this is not considered in MRP as the screen below
The material has a material group in the material master, please go to the customization transaction OPPR.Input the plant and MRP group, then click the button 'Safety Stock', then the screen below is displayed.
e.g. there is a requirement of safety stock 100, and the 'Share SStk' has the value 100 in the OPPR, then the quantity 100 * 100% = 100 will be used to cover its requirement. Since this can cover the safety stock itself no proposals are needed .
Case 3: No proposals are created for the requirement of PIR (Planned independent requirement)
E.g. Today is 29.09.2011, plus 7 working days forward it goes to 10.10.2011. Since the PIRs lie before this date they are not included in the MRP calculation and no proposals can be created for them.
Case 4: The dependent requirements are not considered in MRP
After checking, it is turned out that the value 1 'Materials for dependent requirements are not planned' in the field 'MRP dep.requirements' of MRP 4 view of the material master as below.Case 5. Sales documents are not considered in MRP
It happens because the field 'No MRP' has value 1 'Requirement not planned, but displayed' in customization transaction OVZG as above for the requirement class of the sales document.If that is blank, the sales document can be planned by MRP. If that has value 2, the sales document doesn't appear in transaction MD04.
To get the requirement class of sales document, check requirement type in field BEDAE of table VBAP, go to customization transaction OVZH as following to find the requirement class by requirement type.
Case 6. The MRP user exit M61X0001 implemented to exclude certain materials in MRP.
Case 7. Some BADIs are implemented to exclude the MRP requirements.
Automatic assignment of Storage Location MRP Area to Material Master
In S/4HANA 2020, it is possible to automatically assign a storage location MRP Area to a material when extending this storage location to a material, and have default values for the MRP fields in the MRP area. This feature allows a storage location to be automatically excluded from MRP or planned separately whenever it is extended for a material.After the profile creation, we need to check the flag Assign Materials Automatically and assign the profile to the MRP Area in the MRP Area customizing (transaction OMIZ).

With this setting in place, whenever we extend storage location 0004 (which is the storage location assigned to the MRP Area) to a new material, it will automatically create the assignment to the MRP Area, with the field values proposed on the profile.













Comments
Post a Comment